Switchable Authorization Checks: SAP Security Notes October 2016
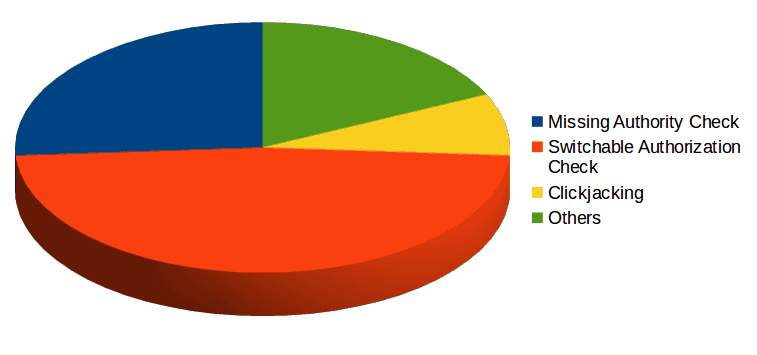
Today, SAP released their monthly security notes. This month, there are 23 new SAP notes that contain new switchable authorization checks in RFC, and 7 SAP notes for missing authorization checks. This month’s security notes also includes 29 note updates from previously published security notes. Taking into account that only 3 notes are considered high priority, it is safe to assume that October is not a ‘risky’ month. Nevertheless, many of this month’s notes require manual activation in order to ensure that they are fully effective in securing SAP. It is highly recommended that Information Security teams review the necessary steps in order to stay protected. The following provides you with an introduction to what must be done in order to properly apply the latest SAP security notes.
Switchable Authorization Checks
Almost half of this month’s notes are related to switchable authorization checks. Historically, this marks the seventh month in a row to include switchable authorization checks notes. How does it work? As most of you may already know, ‘missing authorization checks’ is one of the most common types of vulnerabilities in the SAP Platform. Whenever a new authorization object is added through an SAP note, it could lead to transaction denial if user permissions are not properly updated. When it comes to RFC function modules or critical transactions, authorization checks could lead to business-critical system communication interruption if legitimate users do not have the newly introduced authorization. For these cases, SAP delivers authority changes inactive to ensure that business operations remain undisrupted after support packages or SAP Notes have been technically implemented. This is the second time SAP has published several notes relating to authorization checks in the same month, following 27 notes related to this in November 2014. As explained, “a Switchable Authorization Check can be seen as a mechanism that puts in place the checks for specific authorization objects but disabled until they are explicitly enabled”. It’s essential to understand that applying these security notes is not enough to guarantee that the problem is taken care of. It is very important to enable the authority check through the transaction SACF (Switchable Authorization Checks Framework), available in all software systems based on SAP NetWeaver AS for ABAP 7.0 and higher; and assign the required authorization objects to the corresponding users to avoid communication interruption. Here you can check the minimum service pack required for the SACF framework:
- 740-> SP08
- 731-> SP13
- 730-> SP12
- 720-> SP8
- 711-> SP14
- 710-> SP19
- 702-> SP16
- 701-> SP16
- 700-> SP32
High Priority SAP Notes
Since the last patch Tuesday and today, SAP has delivered three corrections with high priority. Two of them were published today, and one was published September 22nd, out of the monthly publication schedule. Here’s a summary of these outstanding SAP notes:
- Missing Authentication check in message server info service (2331908): despite being an information service, a bug is tagged as high since it affects not only confidentiality but also availability and integrity.
- Denial of service (DOS) in SQL Anywhere Odata Server (2330422): as with any vulnerability that is exploitable through network and without required authentication, the CVSS value is above 7. This is another note that should be implemented with priority.
- XSRF protection for the CCMS Monitoring Console (1511193): A Cross-Site Request Forgery attack.
Improvements for RFC security
The below graph summarizes the types of vulnerabilities fixed this month:
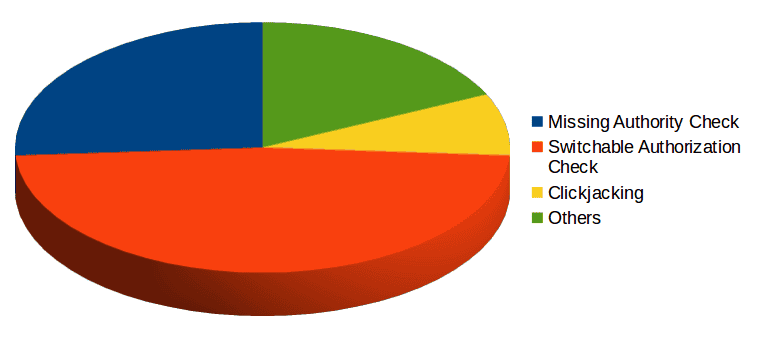
Based on the large amount of switchable authorization check security notes, SAP has also published a consulting note titled updating RFC security note 2078596. Limiting access to Remote Function Calls is possible on SAP NetWeaver AS ABAP 7.4. The unified connectivity (UCON) provides solutions to block remote access to function modules that must not be used remotely. Typically, less than 5% of available RFC function modules in ABAP based software are used in companies for remote RFC communications. These functions used by active business scenarios can be identified, and remote access to all other functions should be blocked. UCON protects remote access to RFC function modules by adding a new layer of access control that is independent of authorization checks. When RFC function modules are called in a system protected by UCON, the framework checks if the RFC function module is included in a white list. If the RFC function module is not included in the UCON default communication assembly (UCON default CA), access is denied and the RFC session is terminated. UCON is configured through transaction UCONCOCKPIT (or transaction UCONPHTL in systems released prior to support package 7). This month, through Security Note 2078596, SAP has updated RFC Security document with latest vulnerabilities ready for whitelisting or activation. As usual, our Security Researchers are recognized in SAP Acknowledgments page. This month, both Matias Mevied and Gaston Traberg have been mentioned as contributors on enhancing SAP Security, for a Cross Site Scripting Report, finally solved in SAP Note 2344441. The Onapsis Research Labs are currently in the process of updating the Onapsis Security Platform to incorporate these newly published vulnerabilities. This will allow you to check whether your systems are up to date with these latest SAP Security Notes, and ensures that those systems are configured with the appropriate level of security to meet your audit and compliance requirements. Stay tuned for next month’s SAP security notes analysis.
